Asynchronous RFT
This example demonstrates how to run RFT in fully asynchronous mode using the GRPO algorithm, Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct model, and GSM8K dataset.
Trinity-RFT supports Asynchronous RFT by running the trainer and explorer in separate processes.
For this purpose, we provide two main configuration files: explorer.yaml and trainer.yaml.
The primary difference between them is that in explorer.yaml we set mode as explore, while in trainer.yaml we set mode as train.
The model weights of the explorer and trainer are synchronized once every sync_interval * batch_size tasks.
Assuming we have a node with 8 GPUs, we allocate 4 GPUs for the trainer and 4 GPUs for the explorer. Key configurations in explorer.yaml are as follows:
# explorer.yaml
project: <project_name>
name: <experiment_name>
mode: explore
checkpoint_root_dir: /PATH/TO/CHECKPOINT/
algorithm:
algorithm_type: grpo
repeat_times: 8
model:
model_path: /PATH/TO/MODEL/
cluster:
node_num: 1
gpu_per_node: 4
buffer:
total_epochs: 1
batch_size: 64
explorer_input:
taskset:
name: gsm8k
storage_type: file
path: /PATH/TO/DATASET/
split: train
format:
prompt_key: 'question'
response_key: 'answer'
rollout_args:
temperature: 1.0
default_workflow_type: 'math_workflow'
trainer_input:
experience_buffer:
name: gsm8k_buffer
storage_type: queue
path: 'sqlite:///gsm8k.db'
explorer:
runner_num: 32
rollout_model:
engine_type: vllm_async
engine_num: 4
synchronizer:
sync_method: 'checkpoint'
sync_interval: 10
trainer:
trainer_config_path: examples/async_gsm8k/verl_config.yaml
Key configurations in trainer.yaml are as follows:
# trainer.yaml
project: <project_name>
name: <experiment_name>
mode: train
checkpoint_root_dir: /PATH/TO/CHECKPOINT/
algorithm:
algorithm_type: grpo
repeat_times: 8
model:
model_path: /PATH/TO/MODEL/
cluster:
node_num: 1
gpu_per_node: 4
buffer:
total_epochs: 1
train_batch_size: 512
explorer_input:
taskset:
name: gsm8k
storage_type: file
path: /PATH/TO/DATASET/
format:
prompt_key: 'question'
response_key: 'answer'
rollout_args:
temperature: 1.0
default_workflow_type: 'math_workflow'
trainer_input:
experience_buffer:
name: gsm8k_buffer
storage_type: queue
path: 'sqlite:///gsm8k.db'
synchronizer:
sync_method: 'checkpoint'
sync_interval: 10
trainer:
trainer_config_path: examples/async_gsm8k/verl_config.yaml
You can run this example with the following command:
bash examples/async_gsm8k/run.sh
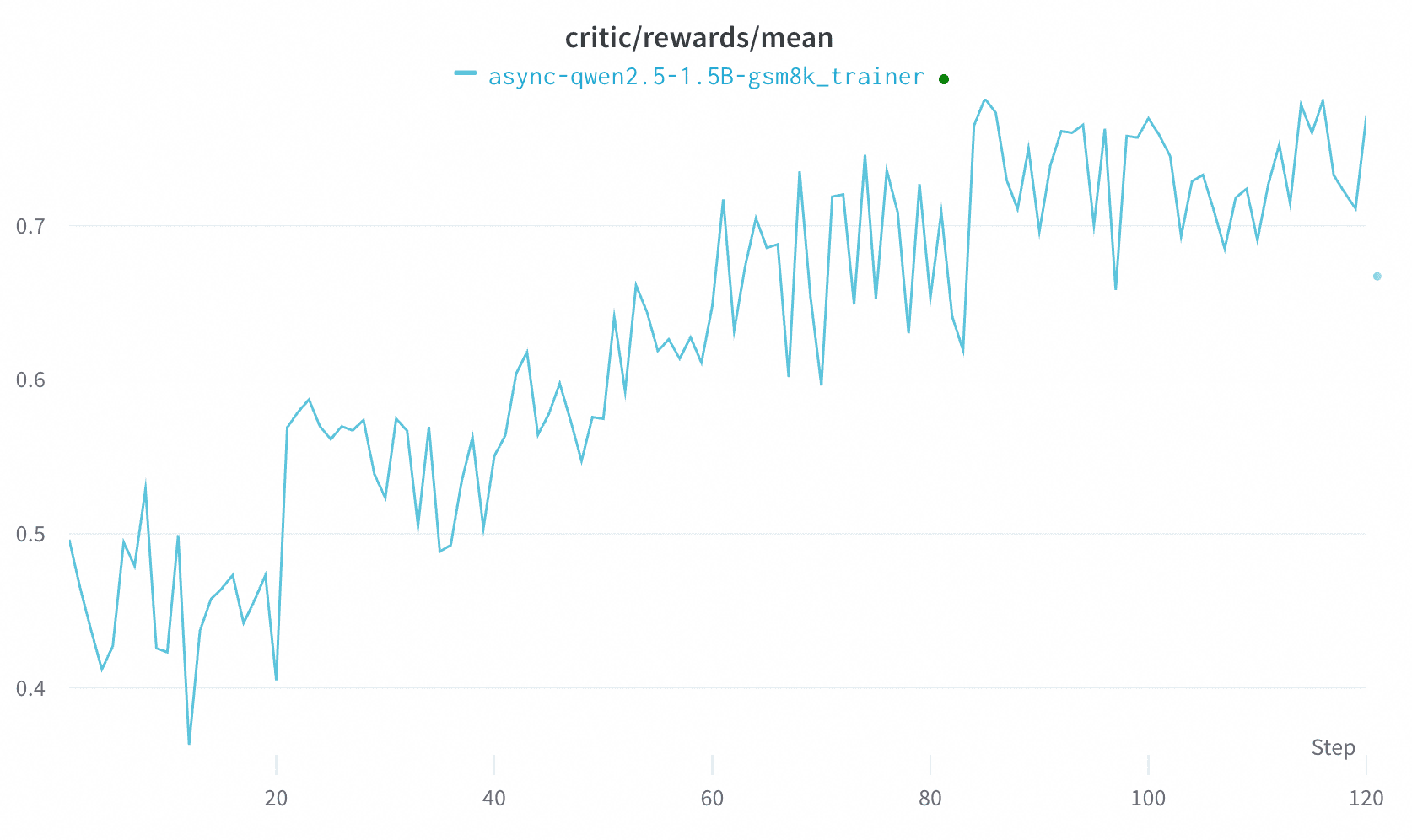
The following plot shows the learning curve of GRPO in the asynchronous mode.
This result should be regarded merely as a baseline, since GRPO is supposed to be an on-policy algorithm. We are continuously investigating other RL algorithms (e.g., OPMD) in the asynchronous mode.
Trinity-RFT also supports dynamic scaling in asynchronous mode. Continuing with the previous example, if an additional machine with 8 GPUs joins the Ray cluster during training, you can launch a new explorer using the following configuration explorer_new.yaml.
# explorer_new.yaml
project: <project_name>
name: <experiment_name>
mode: explore
checkpoint_root_dir: /PATH/TO/CHECKPOINT/
algorithm:
algorithm_type: grpo
repeat_times: 8
model:
model_path: /PATH/TO/MODEL/
cluster: # important
node_num: 1
gpu_per_node: 8
explorer:
name: 'explorer_new' # important
runner_num: 64
rollout_model:
engine_type: vllm_async
engine_num: 8
buffer:
total_epochs: 1
batch_size: 64
explorer_input:
taskset: # important
name: gsm8k
storage_type: file
path: /PATH/TO/DATASET/
format:
prompt_key: 'question'
response_key: 'answer'
rollout_args:
temperature: 1.0
default_workflow_type: 'math_workflow'
trainer_input:
experience_buffer:
name: gsm8k_buffer
storage_type: queue
path: 'sqlite:///gsm8k.db'
synchronizer:
sync_method: 'checkpoint'
sync_interval: 10
# other configs are the same as explorer.yaml
The differences between explorer_new.yaml and explorer.yaml include:
cluster.node_num/gpu_per_node: Specify the cluster configuration for the newly added explorer.explorer.name: The later-started explorer requires a different name than “explorer”, which is the default name for the existing explorer.explorer.rollout_model.engine_num/tensor_parallel_size: Define the engine number and tensor parallel size to optimally utilize GPU resources.buffer.explorer_input.taskset: Provide another task dataset as input for the new explorer.
All other parameters remain the same as in explorer.yaml.