Algorithm 进阶开发#
本指南将会介绍如何将相对复杂的 RL 算法集成到 Trinity-RFT 中。 作为示例,我们引入了由更高级别的 LLM 生成的一些“专家”数据,并提出了一种名为 MIX 的算法,该算法优化以下策略目标:
第一项对应标准的 GRPO 目标,旨在最大化期望奖励。最后一项是在专家数据上定义的辅助目标,鼓励策略模型(policy model)模仿专家行为。\(\mu\) 是一个权重因子,用于控制两项之间的相对重要性。
此流程的可视化如下所示:
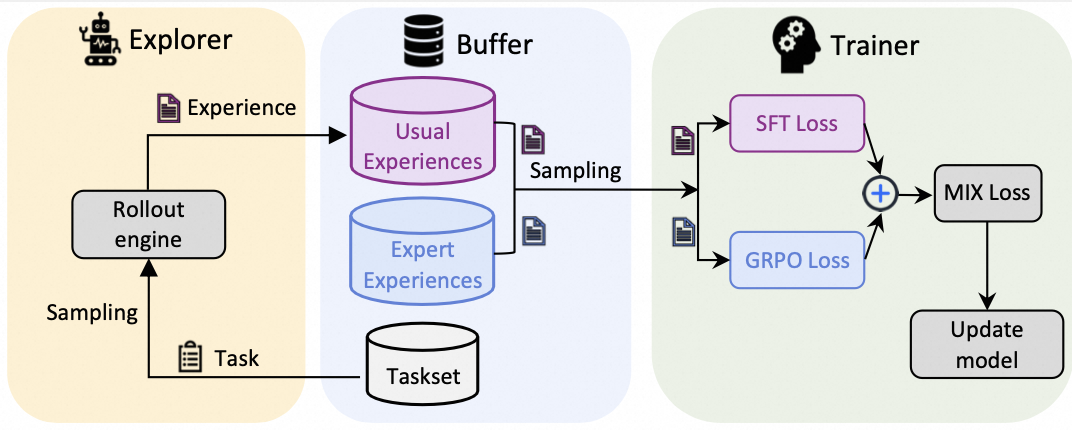
步骤 0:准备专家数据#
我们提示一个强大的 LLM 对一些预定义问题使用 CoT(思维链)过程生成回答。收集到的数据被视为来自专家的一些 experience。我们将它们以 jsonl 格式存储在文件 expert_data.jsonl 中,格式如下:
{
"messages": [
{ "role": "system", "content": "<system_prompt>" },
{ "role": "user", "content": "What is the sum of 4 and 12?" },
{ "role": "assistant", "content": "<think>thinking process...</think>\n<answer>16</answer>" } ]
},
...
专家数据的路径通过 buffer.trainer_input.auxiliary_buffers.sft_dataset 传入,供后续使用。
步骤 1:定义算法#
在 trinity/algorithm/algorithm.py 中,我们引入一个新的算法类型 MIX。
@ALGORITHM_TYPE.register_module("mix")
class MIXAlgorithm(AlgorithmType):
"""MIX algorithm."""
use_critic: bool = False
use_reference: bool = True
compute_advantage_in_trainer: bool = False
can_balance_batch: bool = True
schema: str = "experience"
@classmethod
def default_config(cls) -> Dict:
return {
"repeat_times": 8,
"advantage_fn": "grpo",
"policy_loss_fn": "mix",
"sample_strategy": "mix",
}
步骤 2:定义采样策略#
我们需要在每一步读取两种类型的 experience 数据:普通 experience 和专家 experience。为此,我们定义了一个新的 experience 采样策略,名为 MixSampleStrategy。
class MixSampleStrategy(SampleStrategy):
"""The default sample strategy."""
def __init__(self, buffer_config: BufferConfig, **kwargs):
super().__init__(buffer_config)
self.expert_data_ratio = kwargs.get("expert_data_ratio", 0.5)
self.sft_dataset_name = kwargs.get("sft_dataset_name", "sft_dataset")
tot_batch_size = buffer_config.train_batch_size
expert_batch_size = ceil(self.expert_data_ratio * tot_batch_size)
# experience buffer
usual_buffer_config = copy.deepcopy(buffer_config.trainer_input.experience_buffer)
usual_buffer_config.batch_size = tot_batch_size - expert_batch_size
self.usual_exp_buffer = get_buffer_reader(usual_buffer_config)
if buffer_config.trainer_input.auxiliary_buffers is None:
raise ValueError(
"`buffer_config.trainer_input.auxiliary_buffers` is required in MIX algorithm"
)
# expert experience buffer
expert_buffer_config = copy.deepcopy(
buffer_config.trainer_input.auxiliary_buffers[self.sft_dataset_name]
)
expert_buffer_config.batch_size = expert_batch_size
self.expert_exp_buffer = get_buffer_reader(
expert_buffer_config,
)
async def sample(self, step: int) -> Tuple[Experiences, Dict, List]:
metrics = {}
with Timer(metrics, "time/read_experience"):
usual_exp_list = await self.usual_exp_buffer.read_async()
for exp in usual_exp_list:
if exp.info is None:
exp.info = {}
exp.info["is_expert"] = False
exp.info["step"] = step
expert_exp_list = await self.expert_exp_buffer.read_async()
for exp in expert_exp_list:
# 设置一些 fake rewards and logprobs 以便兼容格式
exp.reward = 0.0
exp.logprobs = torch.zeros_like(
exp.tokens[exp.prompt_length :], dtype=torch.float32
)
exp.advantages = torch.zeros_like(
exp.tokens[exp.prompt_length :], dtype=torch.float32
)
if exp.info is None:
exp.info = {}
exp.info["is_expert"] = True
exp.info["step"] = step
exp_list = usual_exp_list + expert_exp_list
repr_samples = representative_sample(exp_list)
with Timer(metrics, "time/gather_experience"):
exps = Experiences.gather_experiences(
experiences=exp_list,
pad_token_id=self.pad_token_id, # type: ignore [arg-type]
custom_fields=[
CustomField(
source_field="is_expert",
destination_field="expert_mask",
data_type=torch.bool,
),
CustomField(
source_field="step",
destination_field="step",
data_type=torch.int32,
),
],
)
return exps, metrics, repr_samples
这里我们使用 Experiences.gather_experiences 的 custom_fields 参数来添加一个新字段 expert_mask,用以标识该 experience 是否来自专家。这个字段将在策略损失函数中被用来区分普通 experience 和专家 experience。
步骤 3:定义策略损失函数#
我们在 trinity/algorithm/policy_loss_fn/mix_policy_loss.py 中定义一个 MixPolicyLoss 类,它分别计算关于普通 experience 和专家 experience 的两个 losses 之和。
@POLICY_LOSS_FN.register_module("mix")
class MIXPolicyLossFn(PolicyLossFn):
def __init__(
self,
backend: str = "verl",
mu: float = 0.1,
clip_range: Optional[float] = None,
clip_range_low: Optional[float] = None,
clip_range_high: Optional[float] = None,
use_dynamic_bsz: Optional[bool] = None,
ppo_mini_batch_size: int = 1,
ppo_micro_batch_size_per_gpu: int = 1,
ngpus_trainer: int = 1,
train_batch_size_usual: int = 1,
train_batch_size_expert: int = 1,
sft_loss_agg_mode: str = "token-mean",
grpo_loss_agg_mode: str = "token-mean",
) -> None:
super().__init__(backend=backend)
self.mu = mu
self.use_dynamic_bsz = use_dynamic_bsz
self.experience_per_gpu = ppo_mini_batch_size // ngpus_trainer
self.gradient_accumulation = ppo_mini_batch_size // ppo_micro_batch_size_per_gpu
self.train_batch_size_usual = train_batch_size_usual // ngpus_trainer
self.train_batch_size_expert = train_batch_size_expert // ngpus_trainer
self.grpo_loss_fn = PPOPolicyLossFn(
clip_range=clip_range,
clip_range_low=clip_range_low,
clip_range_high=clip_range_high,
loss_agg_mode=grpo_loss_agg_mode,
)
self.sft_loss_fn = SFTLossFn(loss_agg_mode=sft_loss_agg_mode)
def __call__( # type: ignore
self,
logprob: torch.Tensor,
old_logprob: torch.Tensor,
action_mask: torch.Tensor,
advantages: torch.Tensor,
expert_mask: torch.Tensor,
**kwargs,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Dict]:
assert (
len(expert_mask) == logprob.shape[0]
), f"Error: {len(expert_mask)=} != {logprob.shape[0]=}"
n_usual_exp = torch.sum(~expert_mask).item()
n_expert_exp = torch.sum(expert_mask).item()
if self.use_dynamic_bsz:
per_micro_batch_weight_usual = self.experience_per_gpu / (
logprob.shape[0] * self.train_batch_size_usual
)
per_micro_batch_weight_expert = self.experience_per_gpu / (
logprob.shape[0] * self.train_batch_size_expert
)
else:
per_micro_batch_weight_usual = self.gradient_accumulation / self.train_batch_size_usual # type: ignore
per_micro_batch_weight_expert = self.gradient_accumulation / self.train_batch_size_expert # type: ignore
if n_usual_exp > 0:
grpo_loss, grpo_metrics = self.grpo_loss_fn(
logprob[~expert_mask],
old_logprob[~expert_mask],
action_mask[~expert_mask],
advantages[~expert_mask],
**kwargs,
)
grpo_loss = grpo_loss * n_usual_exp * per_micro_batch_weight_usual
grpo_metrics = {
k: v * n_usual_exp * per_micro_batch_weight_usual for k, v in grpo_metrics.items()
}
else:
grpo_loss = torch.tensor(0.0, device=logprob.device)
grpo_metrics = {}
# SFT Loss (expert)
if n_expert_exp > 0:
sft_loss, sft_metrics = self.sft_loss_fn(
logprob[expert_mask],
action_mask[expert_mask],
)
sft_loss = sft_loss * n_expert_exp * per_micro_batch_weight_expert
sft_metrics = {
k: v * n_expert_exp * per_micro_batch_weight_expert for k, v in sft_metrics.items()
}
else:
sft_loss = torch.tensor(0.0, device=logprob.device)
sft_metrics = {}
loss = (1 - self.mu) * grpo_loss + self.mu * sft_loss
metrics = {f"usual/{k}": v for k, v in grpo_metrics.items()}
metrics.update({f"expert/{k}": v for k, v in sft_metrics.items()})
metrics["loss"] = loss.item()
return loss, metrics
@classmethod
def default_args(cls) -> Dict:
return {
"mu": 0.1,
"clip_range": 0.2,
}
步骤 4:运行实验#
通过上述新定义的类和函数,我们可以无需修改其他流程即可运行实验。
下面展示了一个包含关键配置的示例,包括权重因子 \(\mu\)(即 algorithm.policy_loss_fn_args['mu'])以及专家 experience 的批次大小 \(B'\),其值等于 buffer.batch_size、algorithm.sample_strategy_args['expert_data_ratio'] 和 algorithm.repeat_times 的乘积。完整配置请参考 mix_math.yaml。
algorithm:
algorithm_type: mix
repeat_times: 8
sample_strategy_args:
expert_data_ratio: 0.25
policy_loss_fn_args:
mu: 0.1
clip_range: 0.2
sft_loss_agg_mode: "token-mean"
use_dynamic_bsz: True
repeat_times: 8
ppo_mini_batch_size: 256
ppo_micro_batch_size_per_gpu: 4
ngpus_trainer: 4
train_batch_size_expert: 64
train_batch_size_usual: 192
完成以上配置后,可通过以下命令运行实验:
trinity run --config examples/mix_math/mix_math.yaml